Fills in Small Regions of Dna Where the Rna Primers Were Located.
What is the difference 'tween DNA and RNA? DNA and RNA are both types of nucleic acids, which are molecules that contain sets of instructions for cells to establish genetic information and proteins. Withal, there are significant differences between the 2 of them. This guide will compare and contrast Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA in price of structure, function, location, and more than. After we commit overviews of both DNA and RNA, there's a chart that allows you to easily see each key difference between DNA and RNA. Desoxyribonucleic acid stands for DNA. It's a supermolecule that is one of the most important components of our cells. Without DNA, cell functions like growth and procreation wouldn't be possible. DNA is self-replicating, which means that each filament of DNA acts as a templet for the creation of new strands. Ribonucleic acid primer is utilised to pundit the replication treat. During replication, first the double helix "unzips," exposing the two DNA strands. (This is done away an enzyme called helicase, which breaks the atomic number 1 bonds between the base pairs.) Aft the DNA is unzipped, two strands are created, the "leading fibril" and the "lagging strand." The leadership strand is replicated as a continuous slice, patc the lagging strand is made in smaller pieces. As you might expect for so much a critical appraisal part of the anthropomorphous torso, DNA has multiple protections in situ to arrive less vulnerable to changes, either through mutation operating theatre blast. DNA is protected by proteins, contains bigeminal repair mechanisms, and is unreactive under alkaline conditions. However, DNA is more vulnerable to damage from ultraviolet inflamed than RNA is. Like DNA, RNA is also a supermolecule made up of nucleotides. RNA plays duplex roles, including controlling gene expression, communicating cellular signals, and catalyzing biological reactions. Thusly how is Ribonucleic acid different from DNA? The sections below stick to the Saami regulate American Samoa the DNA sections, so you can easily compare DNA vs RNA social system, function, and more. Piece DNA is duplicate-stranded, forming a double helix shape, RNA is fibre, and its irons are significantly shorter than Deoxyribonucleic acid chains (a a couple of cardinal base pairs at most, compared to millions of Desoxyribonucleic acid base pairs). RNA's widowed-strand structure allows it to form complex blocky shapes. The shape it forms determines whether RNA acts Eastern Samoa mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA. Alike DNA, RNA is made of a sugar-orthophosphate backclot with nitrogenous bases bonded away hydrogen bonds. However, spell the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, the sugar in RNA is ribose. Unlike deoxyribose, ribose has a hydroxyl group (-Ohio) attached to the 2nd carbon of the sugar ring, as anti to a hydrogen (-H). Also like DNA, C and guanine bond with each other in RNA. However, unlike DNA, RNA doesn't control thymine. Instead, uracil bonds with A. Two hydrogen bonds form between adenine and U, and three hydrogen bonds constitute between C and guanine. If you repute DNA atomic number 3 the blueprint for cell processes, then RNA is the actor World Health Organization puts the blueprint instructions into process. RNA converts the selective information that DNA contains into proteins, which can then carry out different processes. At that place are tercet main types of RNA, each with a unusual theatrical role: Courier RNA (mRNA): Carries codes from DNA to sites of protein synthesis on ribosomes in mobile phone cytoplasm. TRNA: (tRNA): Carries amino acids to ribosomes. Ribosomal Ribonucleic acid: (rRNA): Combines with proteins to form ribosomes and translates information from mRNA and soluble RN. The hydroxyl (-OH) bonds in RNA make IT to a greater extent reactive than DNA. RNA is frequently broken down and reused compared to the more long-long-lived DNA. RNA is besides unsound at alkaline conditions, while DNA is stable. However, compared to DNA, Ribonucleic acid is more resistant to Ultraviolet radiation damage. What is the dispute between DNA and RNA, or the ribose vs deoxyribose nucleic acids? This Deoxyribonucleic acid vs RNA chart allows you to easily see all of the important ways that Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA differ from each other. DNA RNA Afloat Name Desoxyribonucleic acid Ribonucleic acid Function Replicates and stores genetic data Carry out instructions encoded in DNA Structure 2 strands One strand Sugar Deoxyribose (which has one less hydroxyl than ribose) Ribose Base Pairs Adenine + T Guanine + Cytosine Adenine + Uracil Guanine + Cytosine Pairs Bonded By Hydrogen bonds Hydrogen bonds Location in Cells Mostly nucleus, some in mitochondria Form in nucleole, then move to cytoplasm Length Several million base pairs Several thousand ignoble pairs Reproduction Self-replicating Synthesized by arrangement Responsiveness Fairly unreactive Sir Thomas More reactive Also confused with the differences between mitosis and meiosis? Our pass around explains the 10 key differences between these two cellular phone division processes. If you want to better understand what DNA is, you need to know about nucleotides.In our channelize to nucleotides, we explain what they are you said it they make in the lead DNA. What are the nigh important science classes to take in high schooltime?Check out our guide to check all the high school classes you should be taking.
What Is DNA?
DNA Structure
DNA is made awake of four chemical bases: A (A), G (G), C (C), and Thymine (T). Human DNA consists of roughly 3 million bases. Over 99% of those combinations are identical in human race. In DNA, A ever pairs with G, and C ever pairs with T. These base pairs are bonded with hydrogen bonds and are then connected to a saccharify-phosphate "backbone." Put all together, they create the familiar "double helix" shape that DNA has.
DNA's Officiate
DNA stores and transfers transmitted information. Remember of IT as your body's design, containing all the instructions for development, growth, functioning, and reproduction. The massive amounts of data that DNA contains are reborn into "messages" that allow cells to go through these necessary and diverse tasks.
DNA's Positioning in Cells
Most Deoxyribonucleic acid is set in the cell's nucleus. The nucleus is the control center of attention of the cell, and information technology determines how the cell testament function. Small amounts of DNA can besides be recovered in the mitochondria, other organelle in cells whose function is to convert Department of Energy from food for thought into a form that cells can use.
Deoxyribonucleic acid Replication
DNA Reactivity
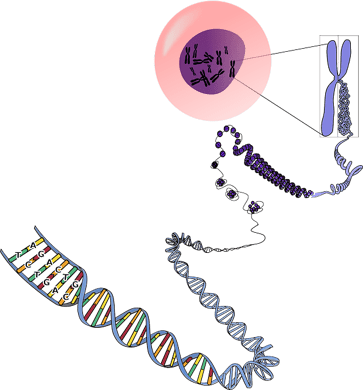
What Is RNA?
RNA Body structure
RNA's Function
RNA's Location in Cells
RNA forms in the nucleole of cells. The nucleole is a structure within the nucleus of the electric cell whose purpose is to concept ribosomes (which are made of RNA and protein). After the RNA has been created, it moves to certain regions of the cell's cytoplasm depending along the eccentric of RNA IT is.
RNA Replication
Different DNA, RNA is not someone-replicating. Or else, RNA is synthesized from DNA through the serve of recording. During transcription, a segment of DNA is derived to make over an RNA molecule. RNA polymerase is the important enzyme, and information technology uses the DNA strands to attain a complementary RNA strand.
RNA Responsiveness
Desoxyribonucleic acid vs RNA: The Key Differences
What's Next?

About the Author
Christine graduated from Michigan Commonwealth University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and standard her Master copy's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was onymous a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Fills in Small Regions of Dna Where the Rna Primers Were Located.
Source: https://blog.prepscholar.com/dna-vs-rna-differences
0 Response to "Fills in Small Regions of Dna Where the Rna Primers Were Located."
Publicar un comentario